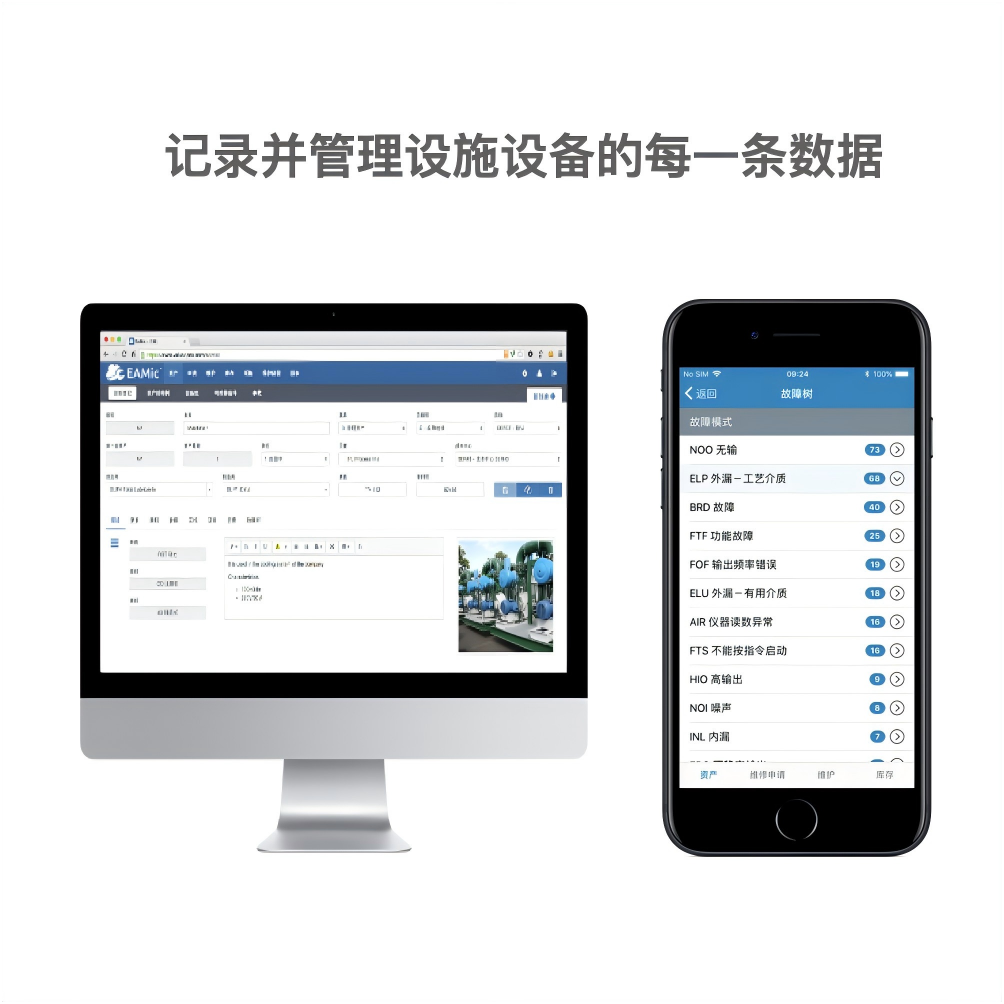
The Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) system, centered on the full lifecycle management of assets, has a scope far beyond traditional equipment maintenance. A complete EAM system typically covers the following five interconnected and complementary content modules, jointly supporting the overall framework of enterprise asset management.

This is the core and foundation of the EAM system, focusing on the "physical entity" of the asset itself.
Asset Register Management: Establishes a unique, complete "electronic file" for all asset equipment, including identity information, technical parameters, financial information, supplier details, drawings/documents, etc.
Equipment Hierarchy Structure: Establishes hierarchical relationships between equipment and components, systems and subsystems, clearly displaying the asset structure.
Technical Condition Management: Records and tracks changes in equipment technical condition, modification history, and performance ratings.
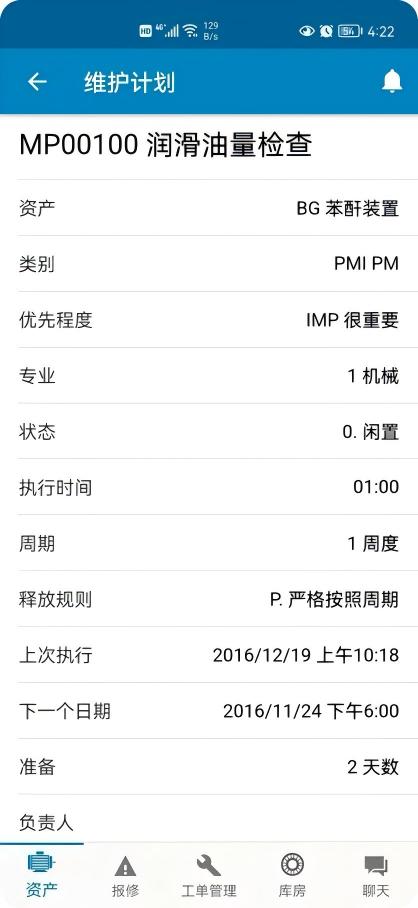
This is the most active and core business process module of the EAM system, focusing on how to maintain and restore the "functional state" of assets.
Work Order Management: The "engine" driving all maintenance activities, covering the entire process from request, planning, approval, dispatch, execution, acceptance, to feedback.
Maintenance Strategy Management: Supports multiple maintenance modes, including corrective, preventive, and predictive maintenance.
Resource Scheduling: Manages human, tool, and external service resources related to maintenance activities.
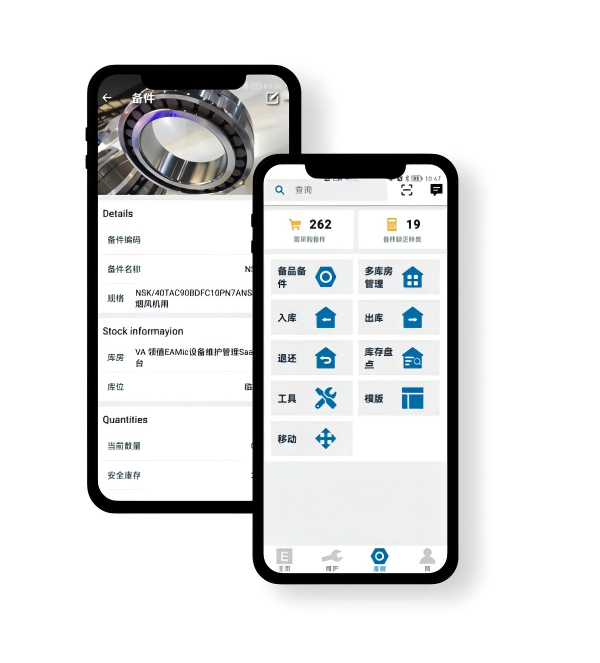
This is the logistical support system for maintenance management, ensuring the timely supply of "ammunition."
Inventory Control: Manages spare parts receiving, issuing, transferring, and counting; sets safety stock and reorder points.
Procurement Management: Integrates with work order and inventory modules, automatically generating purchase requests, tracking purchase order status.
Supplier Management: Establishes supplier files and evaluates their performance.
This is the "brain" of the EAM system, responsible for monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing, focusing on the "economics" and "effectiveness" of asset management.
KPI Monitoring: Tracks key performance indicators like OEE, MTBF, MTTR, Planned Maintenance Percentage, Inventory Turnover Ratio in real-time.
Cost Accounting & Analysis: Collects and allocates all asset-related costs, calculates the Total Cost of Ownership for individual assets.
Reporting & Data Analysis: Provides multi-dimensional, visual analysis reports, supports reliability analysis, failure mode analysis, and drives continuous improvement.
This is the "red line" and "bottom line" permeating all asset management activities, especially in process industries and heavy-asset sectors.
Safety Management: Manages work permits, lockout-tagout, safety procedures, and incident records.
Compliance Management: Manages statutory inspection plans, generates compliance reports, and easily handles audits.
Risk Management: Develops maintenance strategies based on risk, identifying and managing potential operational and financial risks related to assets.
These five areas together constitute a complete EAM management system: asset information is the foundation, maintenance execution is the core, inventory materials are the guarantee, performance/cost is the guide, and safety/compliance is the prerequisite. They are closely connected through data flows and workflows, forming a closed-loop continuous improvement system. The goal is to maximize asset effectiveness and minimize its total lifecycle cost while ensuring safety and compliance, thereby creating maximum value for the enterprise.